General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Embrace enhanced data protection
Data plays a pivotal role in every aspect of our lives, from personal communications to business operations. However, the rising importance of data has also aroused awareness about privacy and security.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) emerged as a comprehensive data protection law to address these concerns and safeguard individuals' privacy rights within the European Union (EU).
In this blog, we will cover:
- What is GDPR?
- Who does GDPR apply to?
- What are GDPR principles?
- What are GDPR requirements?
- What are the consequences of non-compliance?
- Biggest GDPR fines
- Comply with GDPR in 8 steps
- How usecure can help you increase staff GDPR awareness
What is GDPR?
GDPR was enacted on May 25, 2018, by the EU to replace the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC. It was designed to protect the personal data and privacy of EU citizens and residents while harmonizing data protection laws across EU member countries.
GDPR represents a milestone in data protection legislation, setting a new standard for safeguarding personal data within the EU and beyond. Its primary aim is to empower individuals with more control over their personal information while placing greater accountability on organisations that process such data.
Who does GDPR apply to?
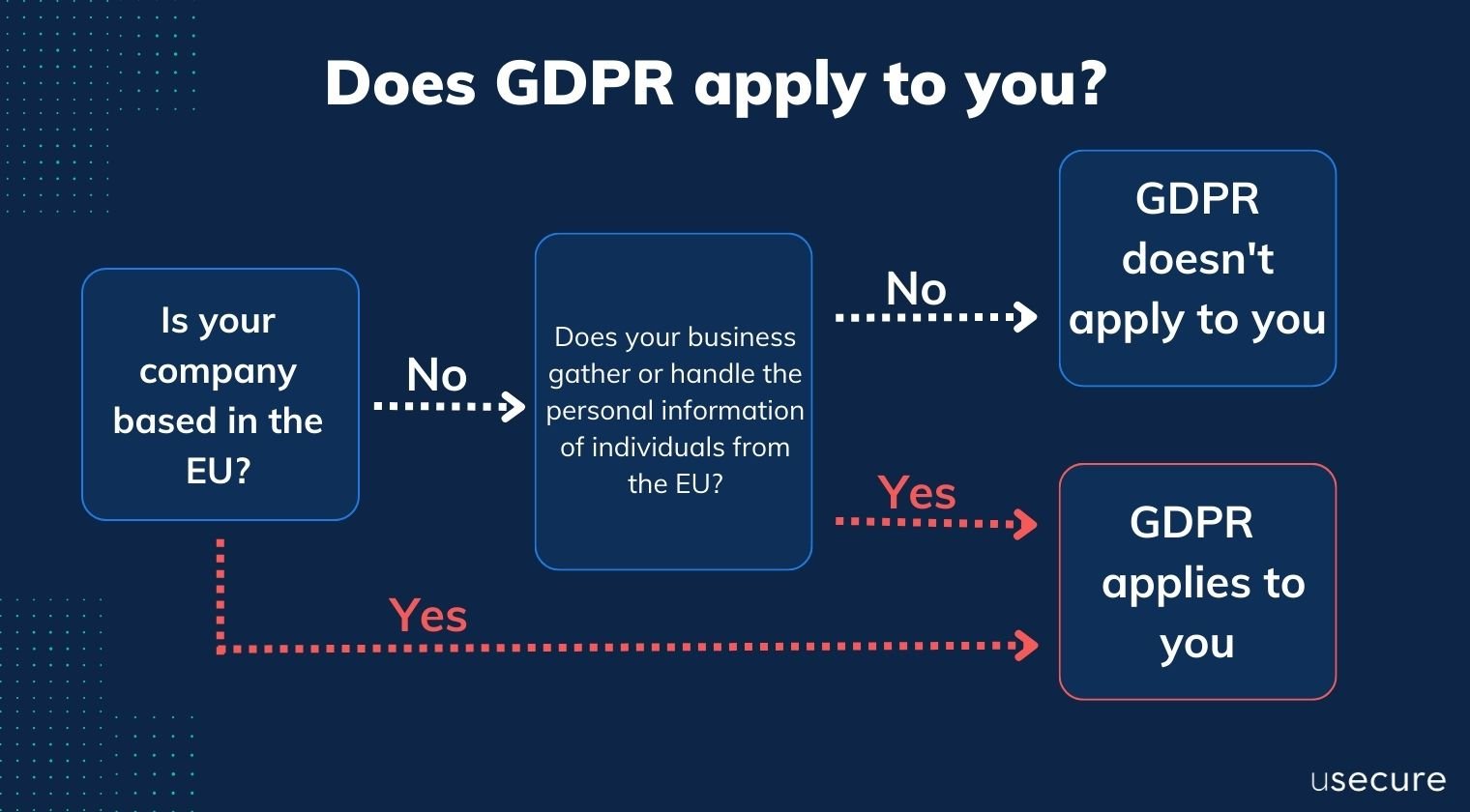
GDPR applies to all 27 members of the EU. However, it not only applies to companies within the EU but also affects businesses outside the EU that process data related to EU citizens.
Any organisation regardless of its location, that handles the personal data of EU citizens falls under the GDPR's jurisdiction if it meets the criteria outlined in Article 3 (Territorial scope). This extraterritorial scope is intended to ensure that individuals' data rights are protected and that businesses worldwide take data privacy seriously.
As a result, many businesses outside the EU have had to assess their data processing practices, update their privacy policies, and implement necessary measures to comply with the GDPR's requirements.
.jpg?width=1520&height=840&name=Blog%20Banner%20%20Cover%20(22).jpg)
-
Reminder: Even post-Brexit, UK residents are still covered by the GDPR, as the UK has maintained similar provisions in its UK-GDPR. Nonetheless, there are certain exceptions.
- For instance, organisations with fewer than 250 staff are exempt from most record-keeping duties (refer to Article 30.5). This exemption doesn't apply if the processing of personal data:
-
- poses potential risks to data subjects' rights and freedoms,
- is not occasional,
- involves special data categories as outlined in Article 9,
- contains personal data related to criminal records and offences as mentioned in Article 10.
What are GDPR principles?
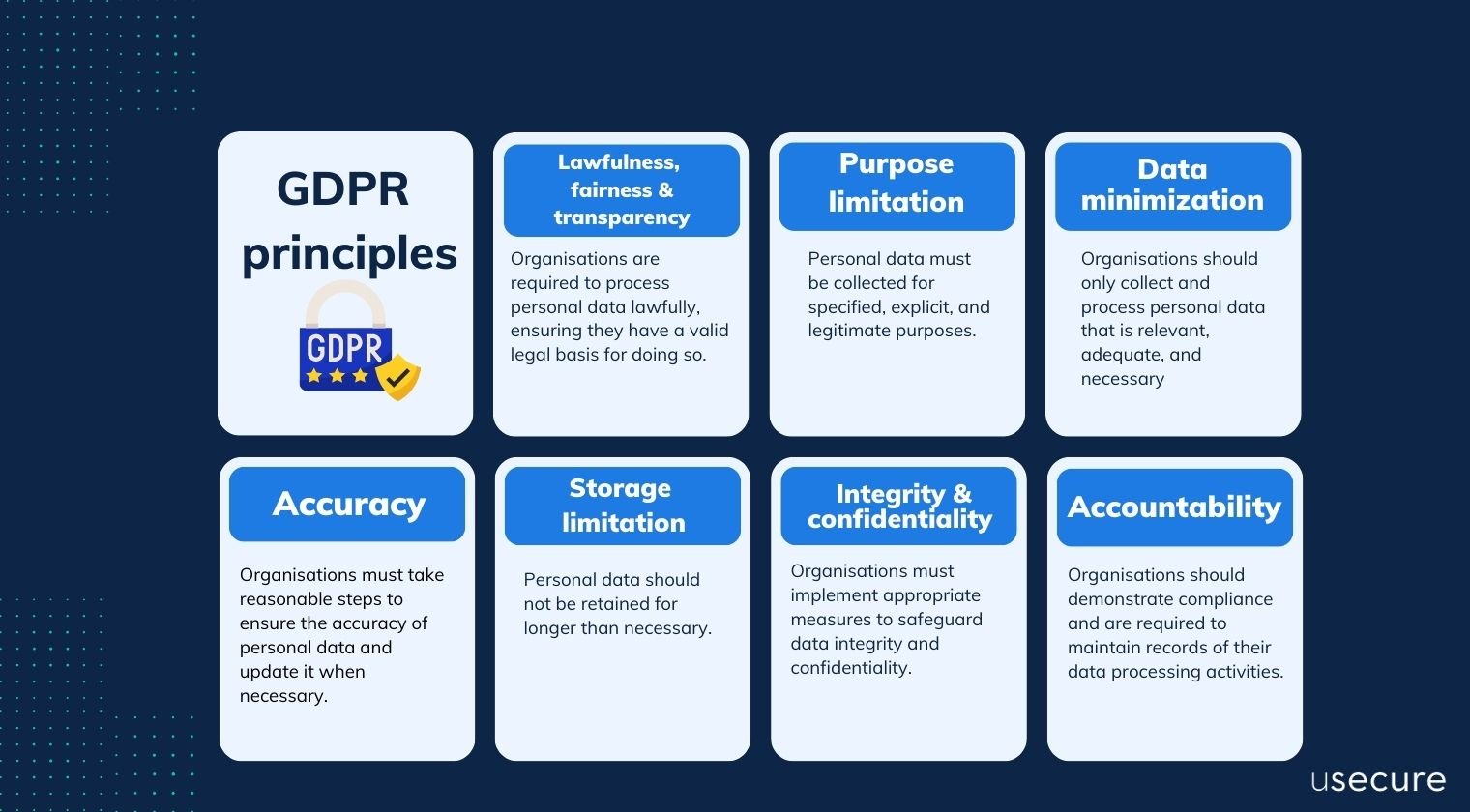
The GDPR encompasses several fundamental principles that organisations must adhere to when processing personal data. These principles reflect the core values of data protection and are outlined in Article 5 of the regulation.
-
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
Organisations are required to process personal data lawfully, ensuring they have a valid legal basis for doing so. They must be transparent about their data processing activities, informing data subjects about the purposes and lawful grounds for processing their data. -
Purpose limitation
Personal data must be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Organisations cannot process data for reasons that are incompatible with the original purpose for which it was collected. -
Data minimization
GDPR advocates for data minimization, meaning that organisations should only collect and process personal data that is relevant, adequate, and necessary for the intended purpose. Unnecessary data collection is discouraged. -
Accuracy
Organisations must take reasonable steps to ensure the accuracy of personal data and update it when necessary. Inaccurate data should be rectified or erased without delay. -
Storage limitation
Personal data should not be retained for longer than necessary to fulfil the purposes for which it was collected. Organisations are required to establish data retention periods based on specific criteria and legal requirements. -
Integrity and confidentiality
GDPR emphasises the need to protect personal data from unauthorised access, alteration, or disclosure. Organisations must implement appropriate technical and organisational measures to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality. -
Accountability
Perhaps one of the most significant principles of GDPR is accountability. Organisations are responsible for demonstrating compliance with the regulation's principles and are required to maintain records of their data processing activities.
What are GDPR requirements?
The GDPR encompasses 11 chapters that organisations must adhere to when processing personal data. These principles reflect the core values of data protection.
Chapter 1: General Provisions (Articles 1-4)
- The first chapter provides the scope and objectives of the regulation, as well as definitions of key terms used throughout the GDPR.
Chapter 2: Principles (Articles 5-11)
- Chapter 2 outlines the principles that should govern the processing of personal data.
Chapter 3: Rights of Data Subjects (Articles 12-23)
- Chapter 3 sets out the rights of individuals regarding their personal data, including the right to be informed, access, rectification, erasure (right to be forgotten), restriction of processing, data portability, and objection.
Chapter 4: Controller and Processor (Articles 24-43)
- Chapter 4 defines the responsibilities of data controllers and data processors. In the case of a personal data breach, the controller shall notify the supervisory authority not later than 72 hours after having become aware of it. This chapter also covers the implementation of appropriate measures to ensure data protection and privacy.
Chapter 5: Transfers of Personal Data to Third Countries or International Organizations (Articles 44-50)
- Chapter 5 covers the conditions for transferring personal data outside the European Union to ensure an adequate level of protection.
Chapter 6: Independent Supervisory Authorities (Articles 51-59)
- Chapter 6 outlines the role and powers of independent data protection authorities in each EU member country. These authorities are responsible for overseeing and enforcing the application of the GDPR within their respective jurisdictions.
Chapter 7: Cooperation and Consistency (Articles 60-76)
- Chapter 7 promotes collaboration between supervisory authorities and ensures that data protection is enforced in a harmonised manner, particularly in cases involving multiple EU member countries or data processing activities that extend beyond national borders.
Chapter 8: Remedies, Liabilities, and Penalties (Articles 77-84)
- Chapter 8 outlines the consequences and measures that can be taken in case of non-compliance with the GDPR, as well as the rights of data subjects to seek remedies and compensation for violations of their data protection rights.
Chapter 9: Specific Data Processing Situations (Articles 85-91)
- Chapter 9 addresses specific data processing situations, including processing for journalistic purposes, research, and archiving purposes, and the derogations for specific national rules.
Chapter 10: Delegated and Implementing Acts (Articles 92-93)
- Chapter 10 deals with the possibility of the European Commission adopting delegated and implementing acts to supplement the GDPR.
Chapter 11: Final Provisions (Articles 94-99)
- The last chapter includes miscellaneous provisions, such as the delegation of power to the European Commission, the Committee procedure, and the authorisation for EU members to maintain or introduce further conditions for specific data processing situations.
What are the consequences of non-compliance?
The fines under GDPR are structured to impose a significant impact on non-compliance. These fines are categorised into two tiers based on the severity of the breach.
-
1st tier
For less severe infringements, the penalty can amount to €10 million or 2% of the company's annual revenue from the previous financial year, whichever is greater. -
2nd tier
In cases of more serious violations, the fine can reach a maximum of €20 million or 4% of the company's annual revenue from the preceding year, again depending on which amount is higher.
Biggest GDPR fines
Here are the top 3 biggest GDPR fines by far. They underscore the importance of robust data privacy practices, proactive compliance with international data protection regulations, and the need for businesses to be especially vigilant when handling data related to vulnerable groups.-
€1.2 billion - Meta GDPR fine
The Irish Data Protection Authority (IE DPA) has levied a fine of 1.2 billion euros against Meta Platforms Ireland Limited (Meta IE) after investigating its Facebook service. This penalty, the most significant under the GDPR to date, was for Meta's personal data transfers to the U.S. using standard contractual clauses (SCCs) from 16 July 2020 onwards. Additionally, Meta is now required to align its data transfers with GDPR regulations. -
€746 million - Amazon
On July 16, 2021, Amazon.com received a fine of €746 million ($888 million) from the Luxembourg National Commission for Data Protection (CNDP) for GDPR violations. This penalty came after a collective complaint against Amazon, initiated in May 2018 by 10,000 individuals via the French digital rights organisation, La Quadrature du Net. -
€405 million - Meta GDPR fine
On September 5, 2022, Meta was fined €405m after a two-year investigation by the Irish data watchdog for letting teenagers set up accounts that publicly displayed their phone numbers and email addresses.
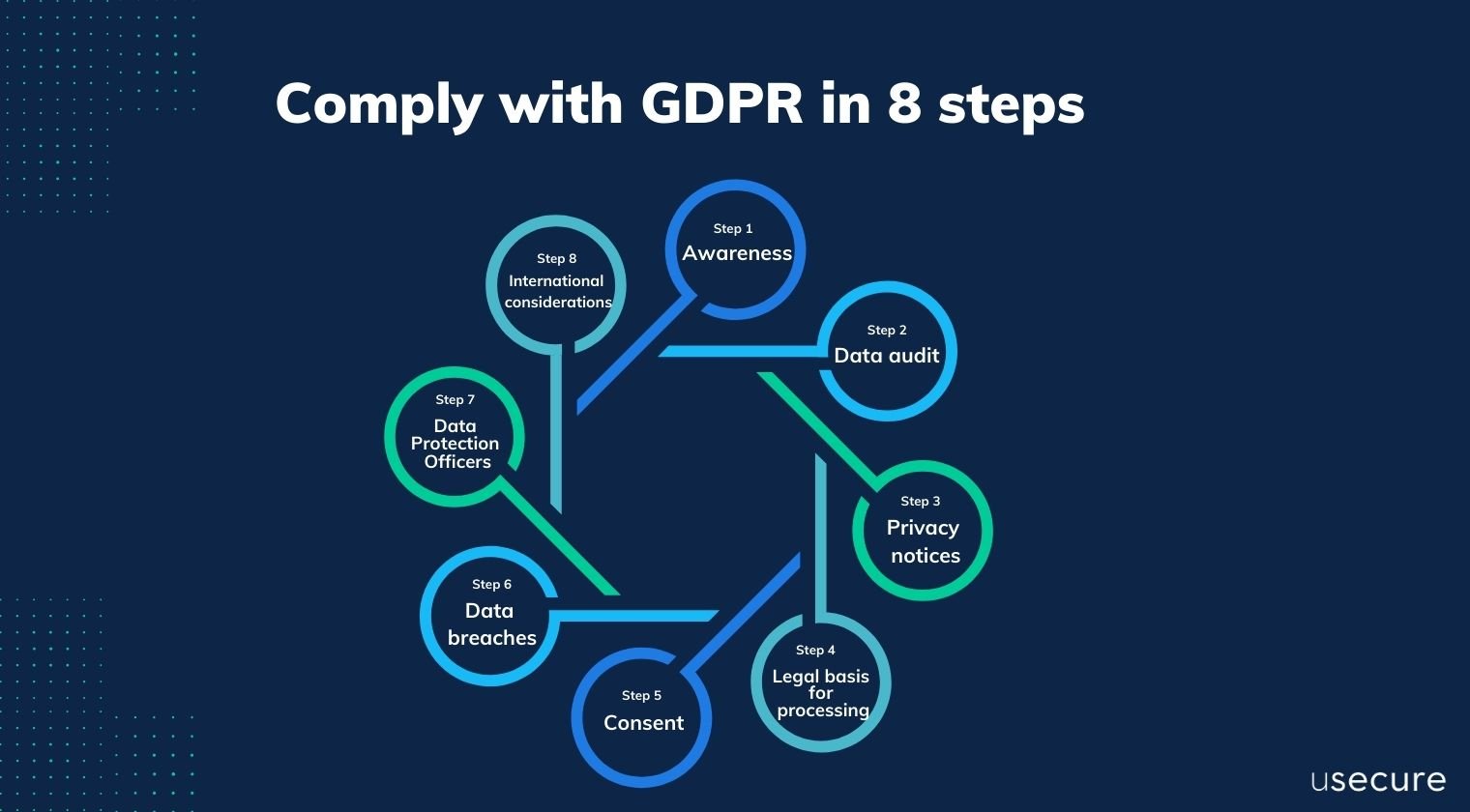
Comply with GDPR in 8 steps
-
Awareness
Ensure that decision-makers and key people are aware of GDPR and its implications. -
Data audit
Document what personal data you hold, where it came from, and who you share it with. -
Privacy notices
Review and update your privacy notices as well as the procedures to handle requests. -
Legal basis for processing
Identify the lawful basis for processing personal data and document it. -
Consent
Review how you seek, record, and manage consent. -
Data breaches
Make sure you have the right procedures in place to detect, report, and investigate personal data breaches. -
Data Protection Officers (DPO)
Appoint a DPO to ensure the organisation adheres to the principles and rules outlined in the GDPR. -
International considerations
Determine your lead data protection supervisory authority if you operate in more than one EU member country.
How usecure can help you increase staff GDPR awareness
At usecure, we provide comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training and policy management tailored to the specific needs of your organisation. Our modules cover a wide range of topics, ensuring that staff are up-to-date with the latest GDPR requirements and best practices.
-
Interactive training modules
usecure's Security Awareness Training provides your employees with interactive sessions that not only educate but also test their understanding of GDPR principles, best practices for protecting personal data, as well as the risks of non-compliance. We make sure your employees are aware of the GDPR and know how to comply with it. -
Customisable content
Understanding that every organisation is unique, we offer customisation options to ensure that training aligns perfectly with company-specific guidelines and policies. -
Policy management
usecure's policy management tool, uPolicy helps you create and manage GDPR policies that are tailored to your specific business needs. We ensure that all your staff know their responsibilities under the GDPR. -
Monitoring staff compliance
usecure helps you monitor staff compliance by tracking employee activity and conducting audits. Thus, you can identify any areas where staff may not be complying with the regulation and take steps to address the issue. -
Continuous learning pathways
With the ever-changing landscape of data protection, our courses are updated from time to time. Employees can take refresher courses or delve deeper into specific areas of GDPR. -
Expert Support
Our team of data protection and cybersecurity experts are on hand to provide guidance, answer questions, and ensure that training sessions are effective and informative.
Stay GDPR-compliant with usecure
With usecure's training platform, organisations can rest assured that their teams are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to uphold GDPR standards, reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring a culture of data protection. Book a demo to learn more or give our 14-day free trial a go today! You can also explore our blog for in-depth insights on effectively navigating global regulations and standards with usecure.

%202023%20India.jpg)
.png)